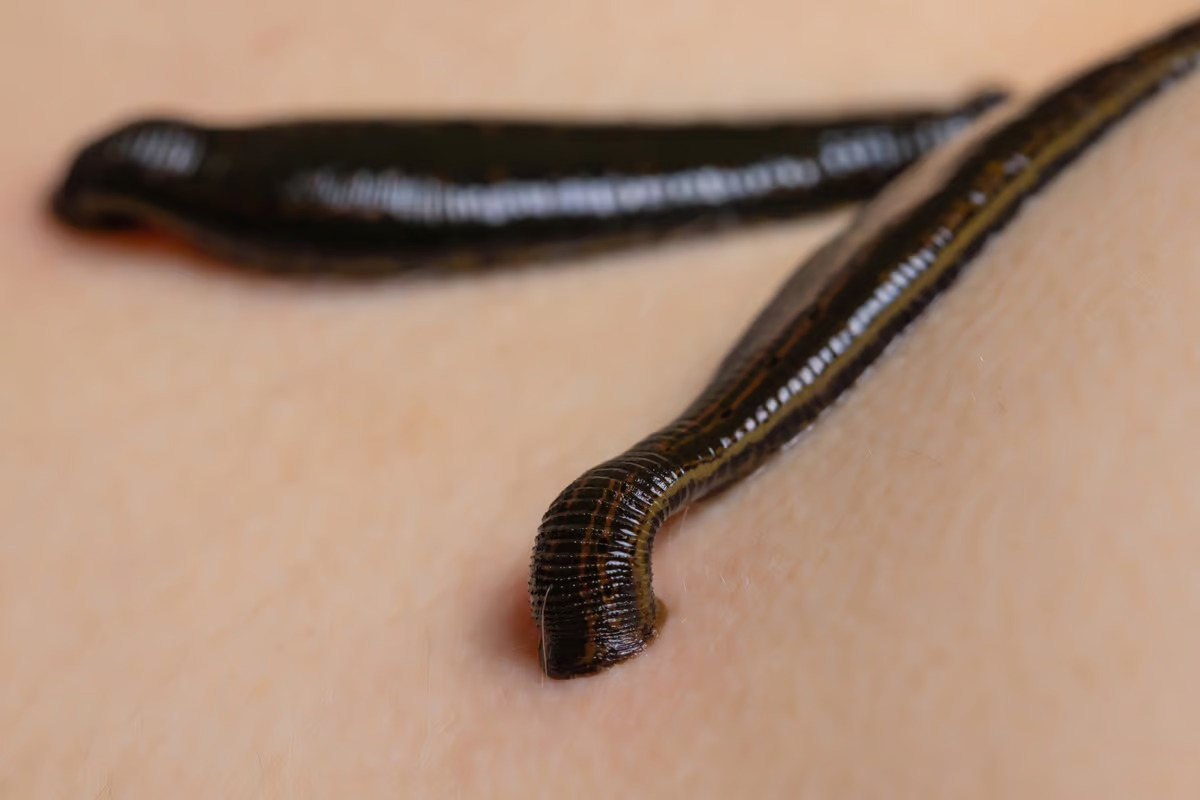
 The bio-inspired device replicates the manner in which leeches (pictured) draw blood through the skin. Depositphotos –
The bio-inspired device replicates the manner in which leeches (pictured) draw blood through the skin. Depositphotos –
Along with not liking the pain involved, a lot of folks (especially children) are just generally uncomfortable with the idea of a needle being pushed through their skin. What’s more, used hypodermic needles pose a health risk to clinicians who may accidentally poke themselves when handling the things.
With such considerations in mind, researchers at Switzerland’s ETH Zurich university recently looked to sanguivorous (blood-feeding) leeches.
These creatures adhere themselves to a host animal’s skin via their suction-cup-like mouths, penetrate that skin with sharp teeth within those mouths, then swallow to create negative pressure which draws out the blood. They also have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva, to keep the blood flowing.
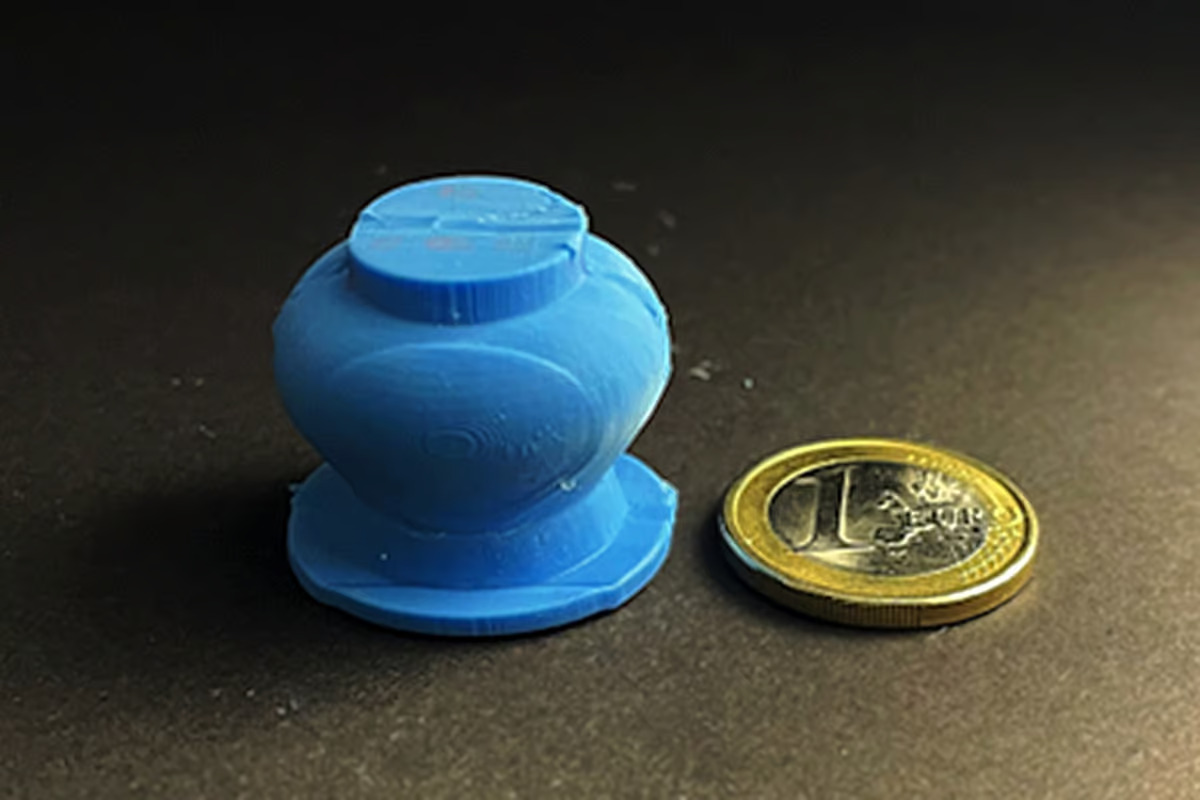

The scientists’ leech-inspired device takes the form of a small silicone suction cup that gets placed on the skin of the upper arm, compressed, then left to do its work.
Instead of having teeth inside, the gadget contains a circular array of 2-mm-long stainless steel microneedles which painlessly penetrate the top layers of the skin. As the compressed cup reverts back to its default shape, it creates negative internal pressure which sucks blood up out of the skin’s capillary veins. That blood is collected in an integrated reservoir which also contains an anticoagulant to ensure that the sample stays in a liquid state.
Once the single-use device is removed from the skin, an included lid is placed over its open end, sealing its contents. A special adapter subsequently allows it to be used in existing laboratory systems that are designed for analyzing blood collected by hypodermic needles. It should be noted that the cup can’t draw as much blood as a needle, but still enough for a wide variety of tests.
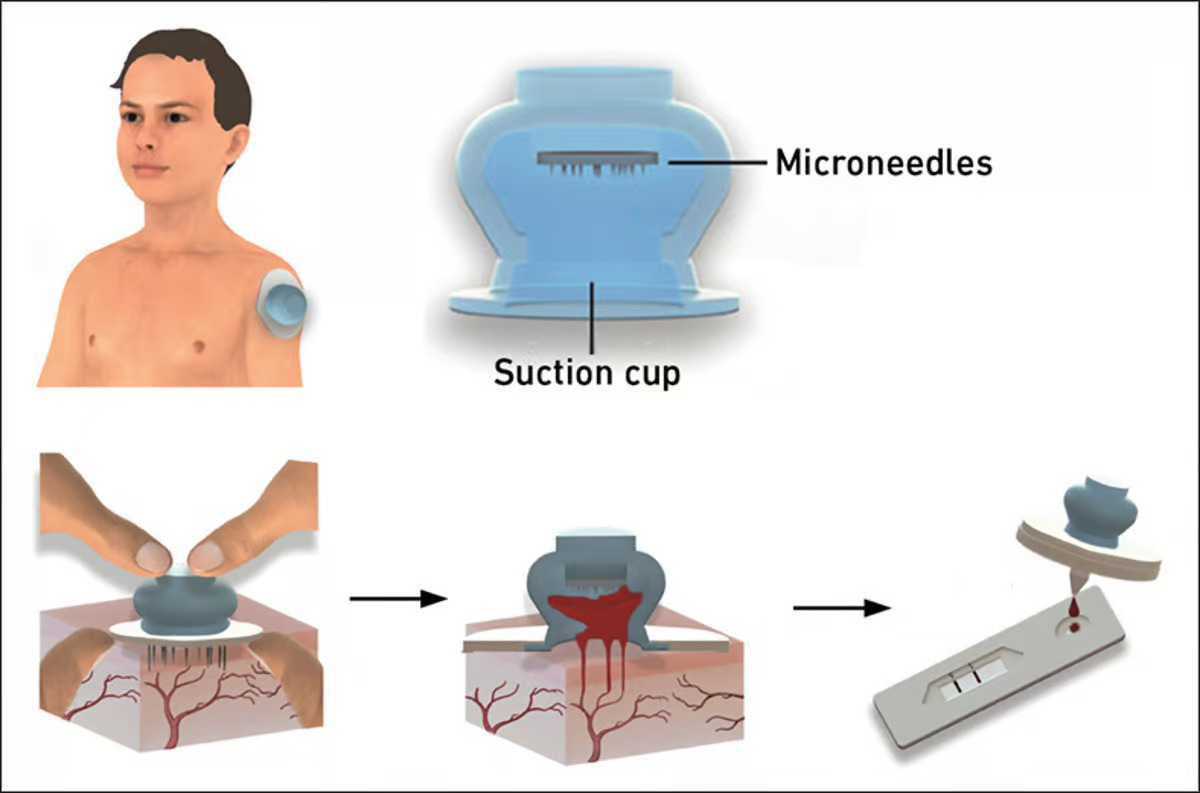
Importantly, because the microneedles are hidden up inside the device, there is very little risk of accidental finger-pokes. The technology is also claimed to be less expensive than traditional hypodermic needles, and to require less training – it could therefore be particularly well-suited to use in resource-limited clinics, such as those in developing nations. A completely biodegradable version is in the works.
The researchers are now looking for partners to help further develop the device, which has already been successfully tested on piglets. In fact, the gadget builds upon another suction-cup gizmo developed by some of the same scientists, which allows certain medications to be applied through the inner lining of the cheek instead of via hypodermic injection.
A paper on the study, which was led by postdoctoral student Nicole Zoratto, was recently published in the journal Advanced Science.
Source: ETH Zurich View gallery – 3 images
–
Tags














![The Ti EDC [everyday carry] Wrench is currently on Kickstarter](https://assets.newatlas.com/dims4/default/0ba225b/2147483647/strip/true/crop/4240x2827+0+3/resize/720x480!/quality/90/?url=http%3A%2F%2Fnewatlas-brightspot.s3.amazonaws.com%2F59%2Fb2%2F6a6fdd0348a8bfdad88bbcefec53%2Fdsc03572.jpeg)



