Evidence suggests tattoos are a very ancient form of human decoration.
Covered in more than 30 tattoos of flowers, animals, and sacred symbols, this 3,000-year-old mummy is one of the most unusual that archaeologist Anne Austin has ever seen. Though other mummies have been found with abstract markings like dots tattooed on their skin, no one had ever seen figurative drawings like these. Austin and her colleagues were stunned. The mummy, found in a village called Deir el-Medina, Egypt, was once a woman who proudly inked sacred wadjet eyes on her neck, shoulders, and back, lotus blossoms on her hips, and cows on her arm. Her village was home to artisans who worked in the nearby Valley of the Kings, where they would have carved elaborate sculptures and inscriptions for pharaohs and gods.
It’s not clear what the tattoos meant nor why this particular woman had so many of them. But Austin speculates that they had religious significance, particularly the eyes and the cows, which may have been a reference to the goddess Hathor. “Any angle that you look at this woman, you see a pair of divine eyes looking back at you,” she told Nature after presenting her work at the American Association of Physical Anthropologists. She first discovered the tattoos when she saw the eye and baboons clearly visible on the mummy’s neck. Suspecting there might be more, she used infrared imaging to see ink that had penetrated the woman’s skin but was no longer visible due to dark resins used for mummification. This is the same technique that scientists used to discover the tattoos on the body of Ötzi the Iceman, a 5,300-year-old body that was accidentally preserved in ice for thousands of years. Ötzi had more than 60 tattoos created with ash that were entirely abstract, mostly horizontal lines on parts of his body where joint swelling suggests that he would have been suffering pain.
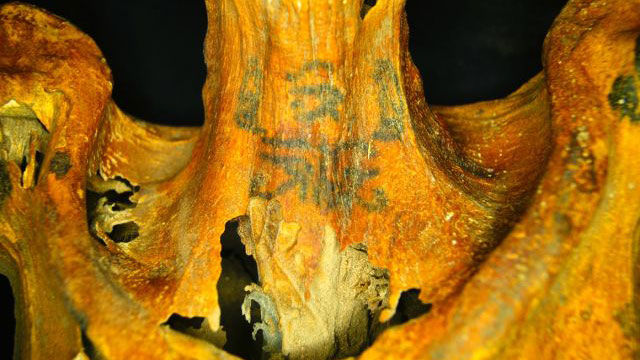
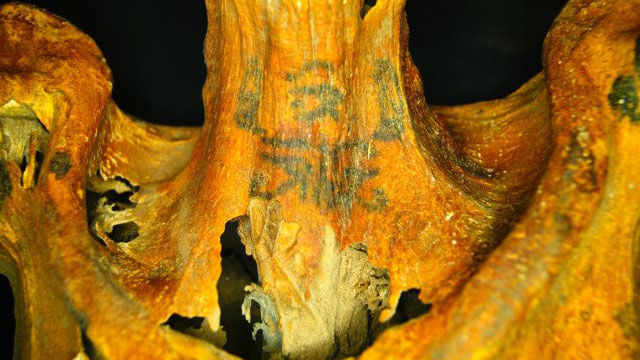
On the 3,000-year-old mummy’s neck, you can see two seated baboons on either side of a wadjet eye (top row), which is a symbol of protection.
The mummy was found in the village Deir el-Medina. Note that some tattoos are visible to the naked eye, but others are on parts of the body that have been blackened by resins used for mummification. Anne Austin

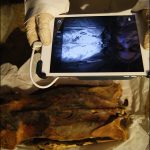
When Austin used infrared imaging, she was able to find many tattoos that were previously hidden. The tattoos on the woman’s back became visible, and Austin and her colleagues used image reconstruction software to correct distortions that were introduced when the mummy’s skin shrank over time. Once the tattoos were stretched, she could clearly see the two cows on the woman’s arm and many other images. Some of the tattoos, she says, were in places where it would have been extremely painful to be tattooed, especially because the process would have been very slow in ancient times. They were also clearly created by someone else, since many were on the woman’s back. These facts suggest the tattoos may have had deep cultural significance. There is also evidence that some of the tattoos were faded, so the woman was probably getting new ink for many years as older tattoos faded.
Humans have been decorating their bodies for tens of thousands of years, and there is evidence dating back to 100,000 years ago depicting workshops where paleolithic peoples mixed up ochres for paints and cosmetics. It appears that tattoos were just part of the typical kit for bodily adornment, and they may be among humanity’s most ancient forms of art.