How do they live? What are they doing for money? To me, this is one of the great mysteries of our time.
I’m certainly not the first person to make note of this shocking statistic. You’ve heard people bemoaning this “labor participation rate,” which is simply the number of working-age men (usually counted as ages 16 to 64) not working or not looking for work, as a percentage of the overall labor force.
It’s true that the pandemic, which of course produced a number of factors that made working more difficult never mind dangerous, pushed the labor participation rate to a record low. But the fact that millions of American males have not been working precedes COVID-19 by decades. In fact, the participation rate for men peaked at 87.4% in October 1949 and has been dropping steadily ever since. It now stands at 67.7%.
As a business journalist for a good portion of those 70-plus years, I’ve looked at thousands of charts and graphs in my life, and I have to say this one is as jaw dropping as it is vexing:
Economists, sociologists, politicians, and cable news pundits each have their pet factors to explain the groundswell of non-work. But after digging down here, I’ve concluded there are many different forces at play. That’s what I want to explore today, which is: how men can live in America without working.
I’m not talking about why men have lost their jobs — factories closing, layoffs, automation, outsourcing jobs overseas, even perhaps women entering the workforce, (in fact, the participation rate by women over the same time period is way up). What I want to get at is how they’re living without holding a “real” job, and by that I mean doing work where one reports income to the IRS, pays taxes and Social Security, etc.
It’s important to note that every man in this group has his own story. They range from mentally ill homeless men who desperately need our help, to the I’m-doing-just-fine-thank-you-very-much, retired early, and former Silicon Valley coder. And there are infinite scenarios in between those two extremes, including, for instance, the many men who have chosen to be stay-at-home dads while their spouses work.
It’s also the case that some men in this group may be unemployed and not seeking work because they’ve given up looking just for now — perhaps waiting for COVID to abate — and will start the search again soon. Here too, society needs to help.
Still, none of this explains decade after decade of falling male employment.
To that end, here to my mind are seven ways men are living without working in America:
-Unemployment insurance
Let’s start with this one because it’s a hot button issue. Conservatives and some liberals too have made the claim that state unemployment aid, coupled with $600 a week from the CARES Act, which was rolled out in March 2020, have reduced men’s need to work. (There are actually a variety of social programs at play, spelled out nicely here by think tank The Century Foundation, which estimates that overall these programs have pumped $800 billion into the economy.) We’ll be getting a good read on whether all this relief did suppress employment now that CARES aid ended for some 7.5 million Americans earlier this month. But as Yahoo Finance’s Denitsa Tsekova reported here and here, states that ended federal aid programs early didn’t see big increases in employment. That may mean these payments really weren’t enough to live off, or not enough to live off by themselves, which speaks to men looking to a combination of sources, like under the table income or family support and possibly some savings (see below).
-Early retirement, pensions, disability and lawsuits
Admittedly, this is a bit of a hodgepodge. And as is the case with many of these categories, hard data is tough to come by, but it is the case that millions of men under 64 are at least partly living off of pensions and 401(k)s. This would include everything from C-suite executives to union members. And don’t forget municipal workers, who make up almost 14% of the U.S. workforce. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, there are some 6,000 public sector retirement systems in the U.S. Collectively these plans have $4.5 trillion in assets, with 14.7 million working members and 11.2 million retirees. The plans distribute $323 billion in benefits annually, and again, some to men who are younger than 64. In fact in almost two-thirds of these plans, if you started working at 25, you max out at 57, a real inducement to stop working — at least at that job of course.
There’s also disability insurance from the Social Security Administration that is being paid to some 9 million Americans who may receive payments many years before retirement age. That’s why I am including disability here, but not plain vanilla Social Security, which you can’t receive until age 62. The maximum disability benefit amount you can receive each month is currently $3,148. (However, the average beneficiary receives about $1,277 per month, according to the law group Social Security Disability Advocates.) Overall, it looks like the SSA pays out some $130 billion in disability annually. That’s not nothing. Then there’s money paid out in medical malpractice each year, smaller true, but still estimated to be in excess of $3 billion. And don’t forget payments from legal settlements and class action lawsuits.
You can argue all day about the right or wrong when it comes to these payouts, but the fact is many of them didn’t exist, or not at this magnitude, decades ago.
-Savings, trading stocks, and bitcoin
Consider now men are living off savings, or from money made in the market or maybe even selling NFTs. How many is it exactly? Who knows, but quite a few for sure. First off, Americans on average do have some money in the bank. Savings as a percentage of disposable income, according to the Federal Reserve of Kansas City, hit a record high of 33% in the spring of 2020 and is still at 14%.
And according to a recent survey by Northwestern Mutual, average personal savings are up over 10% compared to last year, from $65,900 last year to $73,100. Average retirement savings increased 13%, from $87,500 last year to $98,800 today. So there’s that.
Next let’s look at investing — first stocks. It is not irrelevant to this narrative that the S&P 500 has climbed from 2,480 on March 12, 2020 — the day after the World Health Organization declared COVID a pandemic— to 4,441 today, or almost 80%. That’s a huge gain. Much of the action of course has been retail investors and the meme stock boom, as millions of American males stuck at home with nothing to do all day for the past 18 months passed the time trading stocks. Credit Suisse estimates that since the beginning of 2020, “retail trading as a share of overall market activity has nearly doubled from between 15% and 18% to over 30%,” as CNBC reported. How many men were doing this and supporting themselves? Unclear, but upstart trading platform Robinhood (HOOD) — the broker dealer of choice for many of these new investors — reported that it had 22.5 million funded user accounts last month, up from 7.2 million in March of 2020. Let’s just say 15 million new accounts is quite a number.
Now crypto. You can laugh all you want, but the simple fact is that the price of bitcoin is up from $4,861 on March 12, 2000 to $47,763 today, or basically up 10X, (and remember it even hit $64,888.99 this spring). Back to Robinhood, which according to The New York Times, also reported last month that “revenue from cryptocurrency trading fees totaled $233 million, a nearly 50-fold jump from $5 million a year earlier.” (And those are just fees off the trades, mind you.) Bottom line: Folks have made money here. (Of course these guys should be paying taxes on all those stock and crypto gains.)
-Working for cash, aka the under-the-table economy
This one is very tough to measure, too. A study by the Federal Reserve of St. Louis estimates that the average size of the “informal economy” in developed countries is 13% of GDP. Honestly, that could be off by many percentage points, but just to give you a ballpark, GDP in the U.S. this year is about $22 trillion. So 13% of that is $2.86 trillion. As it turns out, $2 trillion-plus, is a number that has been thrown around quite a bit (here and here for instance) when it comes to estimating the size of the cash economy in the U.S. Even if half that money is paid out to women, that still leaves, say, $1 trillion dollars being made by men in this country off the books. That’s a big chunk of change. Are more people than ever working for cash these days? Again, another question that’s impossible to answer. I would bet it’s not fewer. For example, my electrician Luís just told me he can’t get anyone to work for him anymore — they all want to get paid in cash.
-Living off family members
Just to take one facet, the Pew Research Center reported last year that the pandemic “has pushed millions of Americans, especially young adults, to move in with family members. The share of 18- to 29-year-olds living with their parents has become a majority since U.S. coronavirus cases began spreading [in early 2020], surpassing the previous peak during the Great Depression era. In July, 52% of young adults resided with one or both of their parents, up from 47% in February.” How many of these individuals are males living rent free (and sharing food too), which maybe means they don’t have to work? Who knows, but some. Ditto for males who have moved in with in-laws or siblings. And again, many men are choosing to stay home and take care of kids while their spouses work.
-Illegal work
Front and center here is selling illegal drugs. Sadly, business looks to be booming, that is if overdoses are any sort of measure. According to the Washington Post, overdose deaths hit 93,000 last year, up a stunning 30% from 2019. Most of the overdoses were attributed to opioids; heroin, synthetic opioids like OxyContin and in particular Fentanyl. (This despite drug dealers facing supply chain issues during COVID.) How many Americans are in this business and who are they? A number is almost impossible to come by here, but as for who they are, a government report on drug trafficking arrests from five years ago notes that ”the majority of drug trafficking offenders were male (84.9%), the average age of these offenders at sentencing was 36 years, 70% were United States citizens (although this rate varied substantially depending on the type of drug involved), and that almost half (49.4%) of drug traffickers had little or no prior criminal history.” How big a business is selling drugs in America? Could be as much as $100 billion. I think it’s fair to say that a market that size requires many thousands of employees.
What about other types of crime and criminals, everything from robbers and thieves to prostitutes and pimps? To that point there are some 2 million people incarcerated in the U.S. right now. (We have the highest absolute number and the highest per capita on the planet, and hold some 25% of the world’s total prisoners, according to the ACLU.) Being in prison is another way of living in America without working, I guess. But not counting those locked up, how many bad guys are out there on the street? Conservatively, it has to be thousands and thousands, and speaking to this story, they’re all doing their thing and not participating in the labor force.
-Living off the land
This would include gardening, fishing, hunting, clamming, berrying, and just general foraging. The numbers here seem to be climbing. Here for instance from The Guardian:
“Fishing and hunting license sales increased 10% in California during the pandemic, reversing years of decline. Clamming has grown in popularity for several reasons: people are looking for safe activities to do outdoors, but also some are clamming for subsistence and trying to get money from selling the shellfish (which is illegal without a commercial license).”
Ditto for Washington state, according to The Spokesman-Review:
“From the start of the 2020 licensing year in May through Dec. 31, WDFW [Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife] sold nearly 45,000 more fishing licenses and 12,000 more hunting licenses than 2019. The number of new license holders — defined as someone who hadn’t purchased one for the previous five years — went up 16% for fishing licenses and almost 40% for hunters.”
As for growing vegetables in home gardens, yes, it is up, way up too. Even before the pandemic, there were estimates that a third of American families grew vegetables. Now this, NPR reported last year:
“‘We’re being flooded with vegetable orders,’ says George Ball, executive chairman of the Burpee Seed Company, based in Warminster, Penn.
Ball says he has noticed spikes in seed sales during bad times: the stock market crash of 1987, the dot com bubble burst of 2000, and he remembers the two oil crises of the 1970s from his childhood. But he says he has not seen a spike this large and widespread.
So there you have it. It’s a whole range of ways and means, behaviors and experiences. I’m sure I missed some, too. Again, some non-working men are in dire straits and need our help. Others are living non-working lives without burdening society or others, such as a fireman on early retirement (though some argue municipal employee pensions are too high), or an investor who made a ton of money in the market and called it quits, or maybe a wilderness guy living off the land in Alaska.
And some non-working men are not playing fair. Like getting paid under the table, fudging insurance claims or social programs. Some freeload off relatives. And some engage in overtly illegal behavior like boosting branded goods from chain stores to sell online or dealing heroin.
I would imagine that more than a few of these men create a portfolio of sources, though I’m not sure they really think of it that way. Take for example a hypothetical guy in a rural area who lives with his grandmother rent free, (he does help her with the garden some). This guy also does some cash carpentry work, hunts for game, gets some food off his ex-wife’s WIC and helps his brother sell some weed. Can you get by this way? Some men probably are. Is this the new American way? For some men it probably is.
That example perhaps, and to be sure of all of the above, I think go a long way toward explaining that chart from the beginning of the story, the one that shows the labor participation rate falling off a cliff over the past seven decades. And speaking of charts, another striking one came to mind when I was writing this, which I put here below. It shows U.S. GDP over the same time period as the labor participation rate.
–
Of course, the line on this GDP chart is inversely correlated with the line on the labor participation graph. And I think there is a relationship between the two. Which is to say, the wealthier our nation has become over the decades, the less men are working. Fact is there is just a ton of money sloshing around in our country. And men seem to be able to get their hands on it, whether obtained legally, borrowed, leached off of or stolen.
It seems like working legally to provide for yourself in America is really just one option these days.
This article was featured in a Saturday edition of the Morning Brief on 2021 Sep 18. Get the Morning Brief sent directly to your inbox every Monday to Friday by 6:30 a.m. ET. Subscribe
Andy Serwer is editor-in-chief of Yahoo Finance. Follow him on Twitter: @serwer
(This story was updated to include the points about stay-at-home dads and traders needing to pay taxes.)
- What I think will happen next
- Where the U.S. stands after Afghanistan with China and the world
- Billionaires pay no taxes while workers get no raises
- Answering the great inflation question of our time
- What the Metaverse is and why it matters to you
Follow Yahoo Finance on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, Flipboard, SmartNews, LinkedIn, YouTube, and reddit
Find live stock market quotes and the latest business and finance news
For tutorials and information on investing and trading stocks, check out Cashay
-
 Charlotte Observer
Charlotte ObserverFisherman’s sonar spots mysterious object in Carolinas lake. Here’s what divers found
Add this latest discovery to the list of strange things found in Lake Wylie over the years.
-
 Yahoo Life
Yahoo LifeSamuel Adams’ new beer is illegal in 28 states. Here’s why.
Samuel Adams new Utopias beer is illegal in 28 states.
-
 LA Times
LA TimesBig gap between Pfizer, Moderna vaccines seen for preventing COVID hospitalizations
Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine does a significantly better job of preventing COVID-19 hospitalizations compared with Pfizer’s shot.
-
 Engadget
EngadgetMan who unlocked 1.9 million AT&T phones sentenced to 12 years in prison
The scheme cost the company $201.5 million, according to the Department of Justice.
-
 Yahoo Money
Yahoo MoneyRenting ‘is unaffordable to minimum wage workers in every state,’ study finds
For millions of minimum wage workers, the rent is just too damn high to live in parts of the country, even as policymakers fight for a nationwide “living wage.”
-
 MoneyWise
MoneyWiseA fourth stimulus check isn’t coming from the feds, but may be from your state
Relief payments have been approved in several states. Is yours on this list?
-
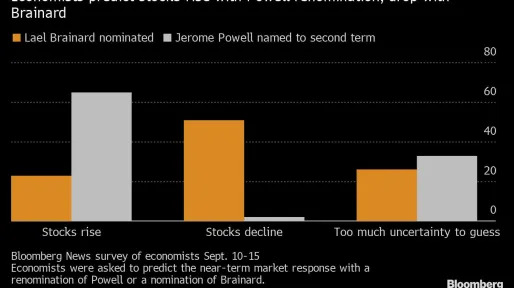 Bloomberg
BloombergStocks to Fall If Biden Drops Powell at Fed, Economists Say
(Bloomberg) — Investors may need to hunker down for a slump in U.S. stocks if President Joe Biden opts for a surprise choice and doesn’t renominate Jerome Powell as Federal Reserve chair.Nearly 90% of the economists surveyed by Bloomberg expect Biden to keep Powell in the job, an overwhelming number that’s risen from June, while Fed Governor Lael Brainard, a Democrat, is seen as the likely choice by 9% of economists surveyed. Former Vice Chair Roger Ferguson was viewed as the pick by 2%. The po
-
 Barrons.com
Barrons.comChina’s Billionaires Are Losing Billions Fast
Grocers already squirreling away Thanksgiving turkeys, Invesco reportedly in merger talks with State Street’s asset management business, Biden reframes his economic agenda as tax relief for working families, and other news to start your day.
-
 The Wall Street Journal
The Wall Street JournalNatural-Gas Prices Surge, and Winter Is Still Months Away
The jump in prices is prompting worries about winter shortages and forecasts for the most expensive fuel since frackers flooded the market.
-
 LA Times
LA TimesAs China’s property giant Evergrande veers toward collapse, its unpaid debts spark protests
China Evergrande is struggling with more than $300 billion in debt. At its Shenzhen headquarters, angry suppliers and investors demand overdue pay.
-
 GOBankingRates
GOBankingRatesStimulus Update: Treasury Issues 6-Month Progress Report Largely Showing Positive Economic Impact
It has been six months since the implementation of the historic American Rescue Plan stimulus relief bill that gave relief to millions of people impacted by the coronavirus outbreak. The Treasury…
-
 FX Empire
FX EmpireWorld shares fall as markets await Fed meeting, taper timeline
NEW YORK (Reuters) – World shares fell on Friday, pressured by concerns over China’s markets, the potential for a U.S. corporate tax hike and an update on the U.S. Federal Reserve’s tapering strategy next week.
-
 MarketWatch
MarketWatchInflation challenges stock-market underpinnings as investors look ahead to Fed meeting
Inflation is unsettling some investors, even if it does prove a transitory feature of the pandemic. “Absolutely inflation is a risk to markets,” Eric Schoenstein, chief investment officer at Jensen Investment Management, said in a phone interview. Wage pressures and supply-chain disruptions tied to COVID-19 are adding costs for companies, some of which are having a “tough time” passing on all the inflation they’re seeing, according to Schoenstein.
-
 The Fiscal Times
The Fiscal TimesWhite House Warns Debt Default Could Cause Recession
The Biden administration on Friday issued fresh warnings about the potential damage that could result from a U.S. debt default. “Hitting the debt ceiling could cause a recession,” a White House letter addressed to state and local governments said. “Economic growth would falter, unemployment would rise, and the labor market could lose millions of jobs.” The recession would hit state and local governments hard, the White House warned. “If the U.S. defaults on its debt — cities and states could exp
-
 The Guardian
The GuardianFears of US government shutdown as debt ceiling game of chicken begins
If neither side budges, US risks default on debt and lowered credit rating, which would cost billions Nancy Pelosi: ‘We’re paying the Trump credit card.’ Photograph: Lenin Nolly/NurPhoto/Rex/Shutterstock Top Democrats are expected to dare Republicans to block a stopgap funding measure, which would trigger the double-barreled fiscal crisis of the US defaulting on its mammoth debt and a shutdown of the federal government, according to two sources familiar with the proposal. The plan being consider
-
 GOBankingRates
GOBankingRatesWhat You Need To Know About the Consumer Price Index
Children learn the concept of inflation the first time they’re forced to listen to a story about how it once cost a quarter to go to the movies. The price of goods and services increases over time as…
-
 Reuters
ReutersWarnings of economic catastrophe come as Congress prepares to debate debt ceiling
WASHINGTON (Reuters) – President Joe Biden’s top aides and local officials nationwide pleaded with U.S. lawmakers on Friday to resolve a government debt showdown that they warned could spark an economic crisis. Congress plans next week to consider legislation that would avoid a default ahead of an October deadline, when the Treasury Department estimates it will no longer be able to pay all of the country’s bills. The White House warned on Friday that a failure by the U.S. Congress to extend the debt limit could plunge the economy into a recession and lead the country to default on its payment obligations.
-
 The Fiscal Times
The Fiscal TimesRestoring SALT Deduction Would Slash Dems’ Tax Hikes for Top Earners: Report
If Democrats’ budget plan restores the full deduction for state and local taxes, it would leave top earners facing much smaller overall tax hikes — or even tax cuts — according to data from the right-leaning Tax Foundation cited by Bloomberg News. The top 1% of earners, those making more than $401,600, would see their after-tax incomes fall by 5% under the House Democratic plan. But if the $10,000 cap on SALT deductibility is eliminated, their after-tax hit would be just 1.9%. Taxpayers making b
-
 Bloomberg
BloombergRuss Dallen, Venezuela Bond Expert and Commentator, Dies at 58
(Bloomberg) — Russell M. Dallen, Jr., a former head of Latin America at Oppenheimer who later went on to become a reference for niche Venezuela legal news around the nation’s complex debt issues, has died, family and friends told Bloomberg News. A lawyer by training, Dallen, 58, was based in Caracas between 2000 and 2007 with Oppenheimer. While living in the country, he purchased the long-time English-language newspaper The Daily Journal and ran it for a brief period before selling and eventually….
-
 Barrons.com
Barrons.comSeptember Is Scary, but Worries About a Stock Market Correction Are Overblown
Budget maneuvering, tax hikes, and a debt-ceiling standoff may hit stocks after a long rally. Don’t fight the Fed and buy any dip, bulls say.
- (For the source of this, and many other equally intriguing and important articles, please visit: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/7-ways-men-live-without-working-in-america-092147068.html)









