Neuralink marches ahead with its first human brain implant trial. Depositphotos
Neuralink marches ahead with its first human brain implant trial. Depositphotos
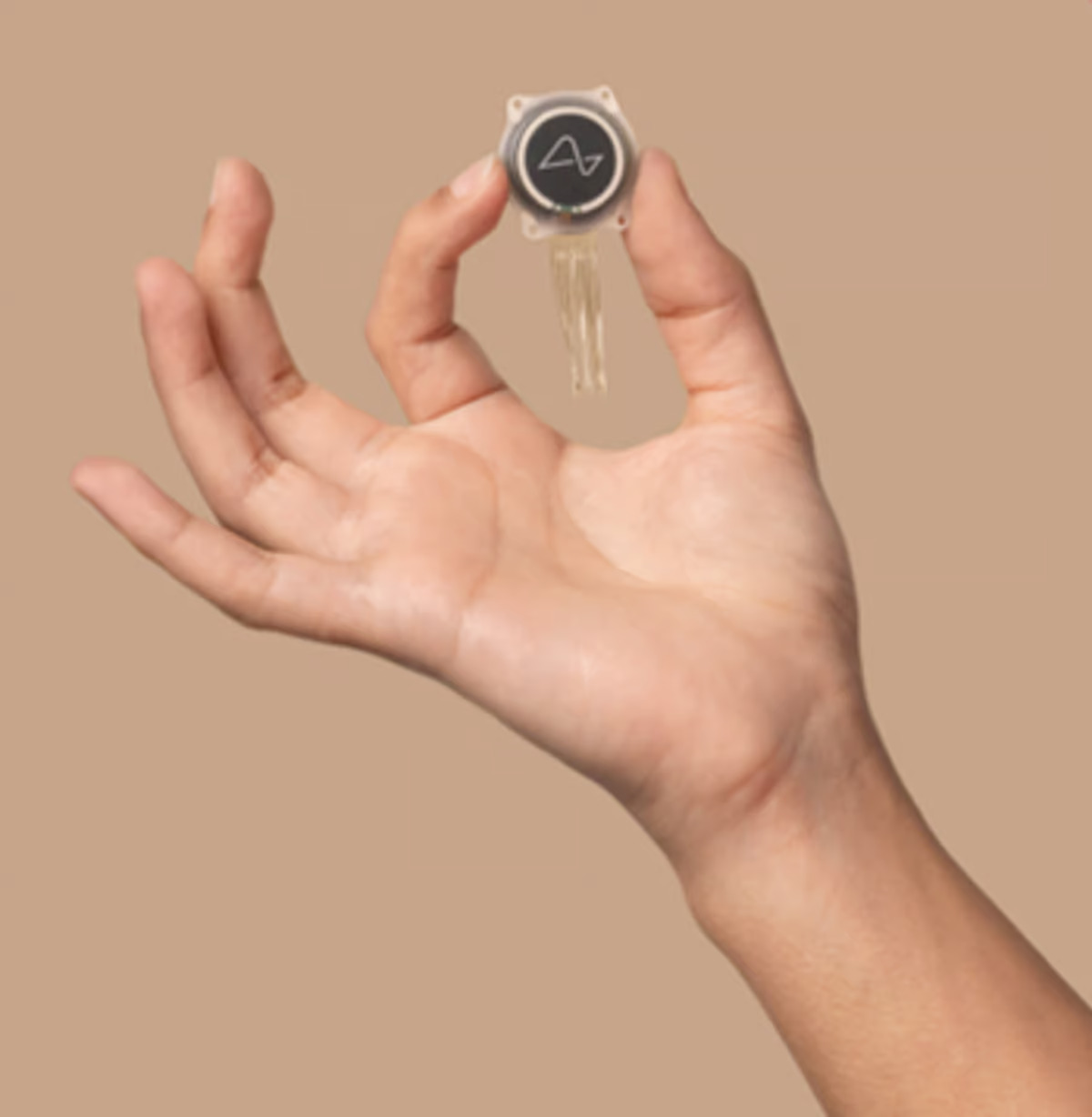
“We are happy to announce that we’ve received approval from the reviewing independent institutional review board and our first hospital site to begin recruitment for our first-in-human clinical trial,” Neuralink said in a statement. “The PRIME Study (short for Precise Robotically Implanted Brain-Computer Interface) – a groundbreaking investigational medical device trial for our fully-implantable, wireless brain-computer interface (BCI) – aims to evaluate the safety of our implant (N1) and surgical robot (R1) and assess the initial functionality of our BCI for enabling people with paralysis to control external devices with their thoughts.
“The R1 Robot will be used to surgically place the N1 Implant’s ultra-fine and flexible threads in a region of the brain that controls movement intention,” the statement continued. “Once in place, the N1 Implant is cosmetically invisible and is intended to record and transmit brain signals wirelessly to an app that decodes movement intention. The initial goal of our BCI is to grant people the ability to control a computer cursor or keyboard using their thoughts alone.”
As expected, the first human trial has strict criteria for potential selection. To be eligible, participants must have quadriplegia (limited function in all four limbs) due to spinal cord injury or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and are at least one year post-injury (without improvement). They must be 22 years or older and have a caregiver. However, anyone in this group who is also prone to seizures, has active implants such as a pacemaker, or requires ongoing MRIs or similar treatments, will be excluded.
The company also invites anyone to join its Patient Registry, with more trials expected to follow.
The study is expected to take six years, with constant monitoring. The first stage, the Primary Study, will include nine at-home and clinic consultations over 18 months. Following this, patients will have to commit to 20 consultations over five years.
Then BCI Research Sessions will be conducted throughout the trial and require two one-hour sessions every week.

In May, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave Neuralink a green light to conduct human trials. This was a swift change of tone from just two months earlier, when the FDA reportedly turned down trial approval, citing safety concerns. (The agency declined to comment at the time.)
“We are excited to share that we have received the FDA’s approval to launch our first-in-human clinical study!” tweeted Neuralink on May 25. “This is the result of incredible work by the Neuralink team in close collaboration with the FDA and represents an important first step that will one day allow our technology to help many people.”
“[The PRIME Study] represents an important step in our mission to create a generalized brain interface to restore autonomy to those with unmet medical needs,” the company added.
Founded in 2016 by Musk, Neuralink’s goal has been to develop a brain chip interface that, when implanted in the skull, can successfully restore movement, communication and potentially vision to people with a broad range of disability.
However, it quickly courted controversy. In February 2022, the company faced claims of poorly managed monkey deaths at its initial testing lab at the University of California, Davis. Neuralink and the college both released statements affirming care had been taken with all live specimens.
“Two animals were euthanized at planned end dates to gather important histological data, and six animals were euthanized at the medical advice of the veterinary staff at UC Davis,” Neuralink’s statement read. “These reasons included one surgical complication involving the use of the FDA-approved product (BioGlue), one device failure, and four suspected device-associated infections, a risk inherent with any percutaneous medical device. In response we developed new surgical protocols and a fully implanted device design for future surgeries.”
However, despite this statement titled Neuralink’s Commitment to Animal Welfare, a damning Reuters report in December 2022 detailed dozens of company documents and interviews with more than 20 current and former employees, which revealed excessive, unnecessary animal cruelty and deaths – 1,500 since 2018 – and many the result of the breakneck speed at which the project was moving.
However, following the Department of Agriculture’s Office of Inspector General opening an investigation probing violations of the Animal Welfare Act, Neuralink was cleared in March.
It’s unknown how many patients will be approved for the historic PRIME Study.
Source: Neuralink
–