–
What was the Silk Road? The history of the Silk Road begins with the Persians of 500 BCE and stretches all the way to the fall of Constantinople in 1453 CE. As one of the most important trade routes in human history, facts about the Silk Road are a gateway into vitally important times – both good and bad. Far from a dusty track in the middle of nowhere, the Silk Road carried priceless goods, art, and knowledge all across Europe and Asia.
Silk Road trivia encompasses everything from the Mongols to the Black Plague to one of the first documented cases of industrial espionage and even the unofficial creed of the US Postal Service. It involves Chinese dynasties, Muslim empires, Mongol hordes, and great European lands. It also shaped the Age of Discovery, eventually forcing explorers to find new ways to the Orient – finding the New World in the process.
Here are some of the most interesting facts about the Silk Road, a place that still shapes the modern world.
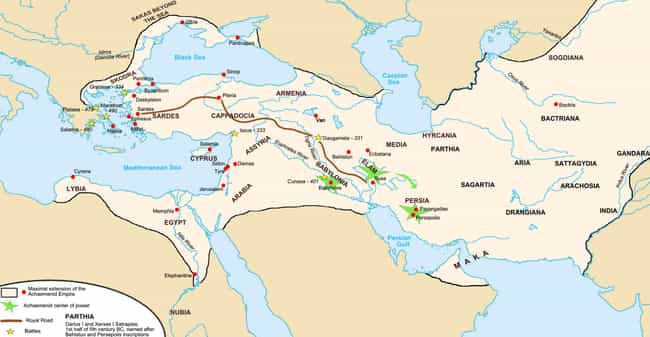
Precursors to the Silk Road Were Built by the Persians
Centuries before the Chinese established the Silk Road, the Persians established a trade route to the Mediterranean. Built by Darius the Great of the Achaemenid Empire in the 5th Century BCE, the Royal Road ran from the ancient city of Susa in modern-day Iran to the western edge of the Empire in Sardis, in modern Turkey. It allowed distant parts of the Empire to trade and communicate with each other in a way nobody ever had until that point. Early Romans improved the infrastructure of the Road, and a few elements of it still exist today.

Persian Couriers Were So Good, They Inspired the US Post Office
The couriers who delivered messages on the Royal Road were so efficient that they could travel almost 1,700 miles in seven days on horseback. In his Histories, Greek historian Herodotus memorialized the Persian riders, writing “There is nothing in the world that travels faster than these Persian couriers. Neither snow, nor rain, nor heat, nor darkness of night prevents these couriers from completing their designated stages with utmost speed.”
A version of this phrase was carved on the James Farley Post Office in New York City, and is traditionally thought of as the US Postal Service’s unofficial motto.
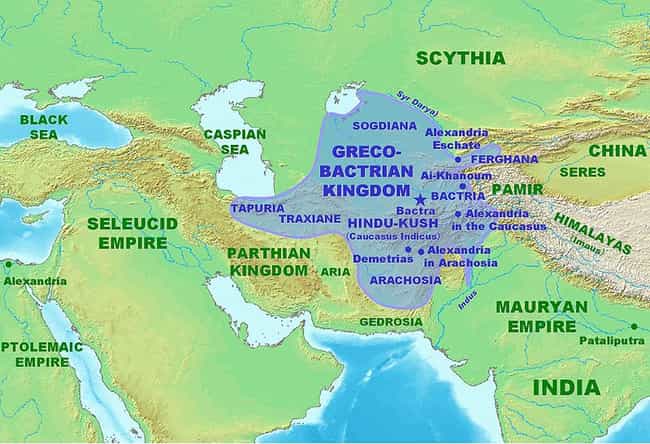
Greece and China Made Contact Shortly Before the Road Was Established
It’s generally believed that first contact between China and Greece came around 200 BCE, in the early days of the Han Dynasty. After conquering the Persians and beating King Darius III, Alexander left behind many of his wounded soldiers in the new cities of Alexandria. Their descendants married the local population, and this Greco-Bactrian culture expanded east, all the way to the borders of what was called Seres – what we now know as China.
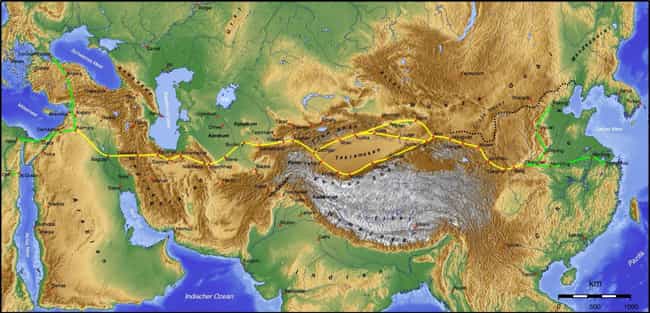
The Road Was Over 4,000 Miles Long
[To read the balance of this extremely interesting article please visit: https://www.ranker.com/list/silk-road-facts/mike-rothschild/]









